Overview
DeliveryMANS, which stands for Delivery MANagement System, is a system for administrators of food delivery applications to efficiently manage the restaurants, customers and deliverymen using the application.
Summary of contributions
-
Major enhancement: Restaurant Manager
-
What it does: Manages all the restaurants in the application database as well as their operations, such as changing of the restaurant’s details, menu and orders.
-
Justification: Restaurants are one of the 3 main stakeholders of a food delivery application, together with customers and deliverymen. A good food delivery application has a large number of restaurants in its database to offer more choices to the users / customers. Changes and updates to these restaurants are frequent: restaurants are often changing their menu; relocation and renaming of restaurants can happen too. Together with the large amount of orders a restaurant receives every day (with the increase in popularity of food delivery services), managing the huge restaurant database can be a hassle for administrators. This Restaurant Manager allows for efficient managing of the large restaurant database through the following highlights that would save administrators much workload and time.
-
Highlights:
-
Restaurant Manager supports EditMode for restaurants: the one interface to view and edit a restaurant’s many attributes, i.e. details, menu and orders. Under EditMode, each attribute of the restaurant will be displayed in its own separate panel so administrators can have a clear view of all the attributes at one glance. Commands that edit the restaurant’s attributes individually, such as
AddFoodCommand,EditDetailsCommandandAddRatingCommand, are also unlocked. This is a feature that involves multiple components of the application (UI, Storage, Order Manager, Logic):-
UI is changed upon entering / exiting EditMode to display / hide the new interface.
-
Every change made to the restaurant in EditMode would have to update that restaurant stored in the database.
-
Certain changes made to the restaurant in EditMode (e.g. changing of name, changing of menu) would have to update the relevant information in each of the restaurant’s orders.
-
Commands unlocked by EditMode should only be accessible in EditMode.
-
-
Restaurant Manager supports auto-tagging of food items as "Popular". An important information that customers wish to be displayed in the application is which food items in a restaurant’s menu are "Popular", i.e. frequently ordered, which would aid them in their choice of food items to order. To determine which food items in a particular restaurant are popular, statistics from previous completed orders, such as number of orders of each food item, would have to be stored. Upon completion of every new order, statistics are updated, the percentage of orders of each food item in the menu is calculated and analysed, and auto-tagged as "popular" if a certain threshold is passed. Auto-tagging saves administrators the workload of manually calculating the statistics and manually tagging each popular food in the huge food database.
-
-
-
Code contributed: [View on RepoSense]
-
Other contributions:
-
Project management:
-
Managed releases
v1.1-v1.4(4 releases) on GitHub -
Managed milestones
v1.2-v1.4(3 releases) on GitHub
-
-
Enhancements to existing features:
-
Wrote tests for Restaurant-side
StorageandLogic(Pull requests #227)
-
-
Documentation:
-
Added documentation on Restaurant-side commands in User Guide (Refer to contributions below)
-
Added documentation on EditMode feature for restaurants in Developer Guide (Refer to contributions below)
-
-
Community:
-
Reported bugs and suggestions for other teams in the class (Reported bugs in PED)
-
-
Contributions to the User Guide
Given below are sections I contributed to the User Guide. They showcase my ability to write documentation targeting end-users. |
Restaurant commands
Commands in the restaurant context
Adding a restaurant: add
This command adds a restaurant to the restaurant database.
Format: add n/NAME l/LOCATION [t/TAG]…
-
LOCATIONcan only be one of the following locations: Jurong, Tuas, Woodlands, Bishan, City, Marina, Changi, Punggol.
Example: add n/KFC l/Jurong t/FastFood
Deleting a restaurant: delete
This command deletes the restaurant at the specified index in the restaurant list from the restaurant database.
Format: delete INDEX
-
INDEXmust be a positive integer from 1 to n, the number of restaurants in the restaurant list.
Example: delete 1
|
Note:
|
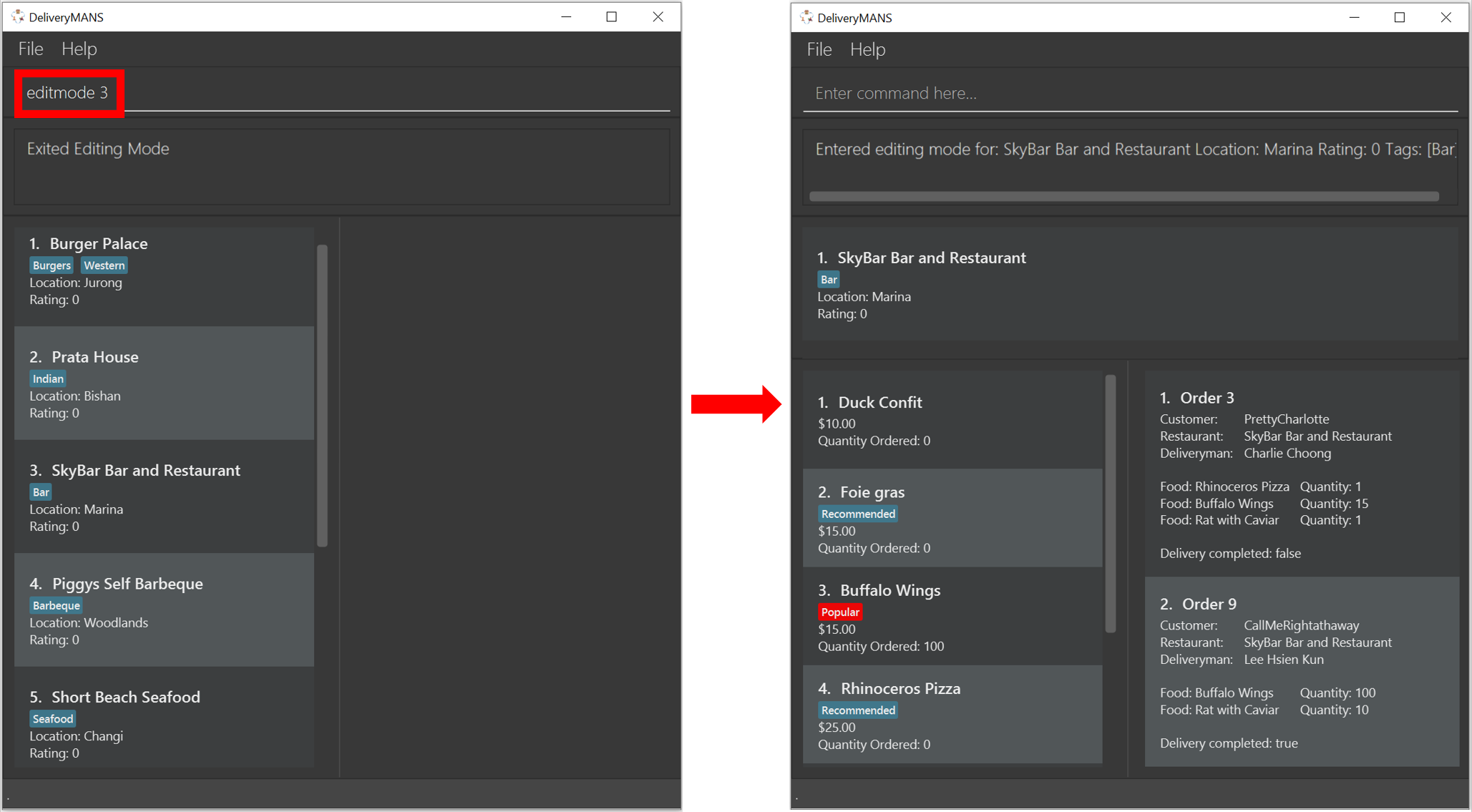
Entering EditMode: editmode
This command enters EditMode for the restaurant identified by the specified index in the restaurant list. Displays the restaurant’s details, menu and current orders. Unlocks commands for editing details, adding and removing of food items in the menu, and adding of rating.
Format: editmode INDEX
-
INDEXmust be a positive integer from 1 to n, the number of restaurants in the restaurant list.
Example: editmode 3
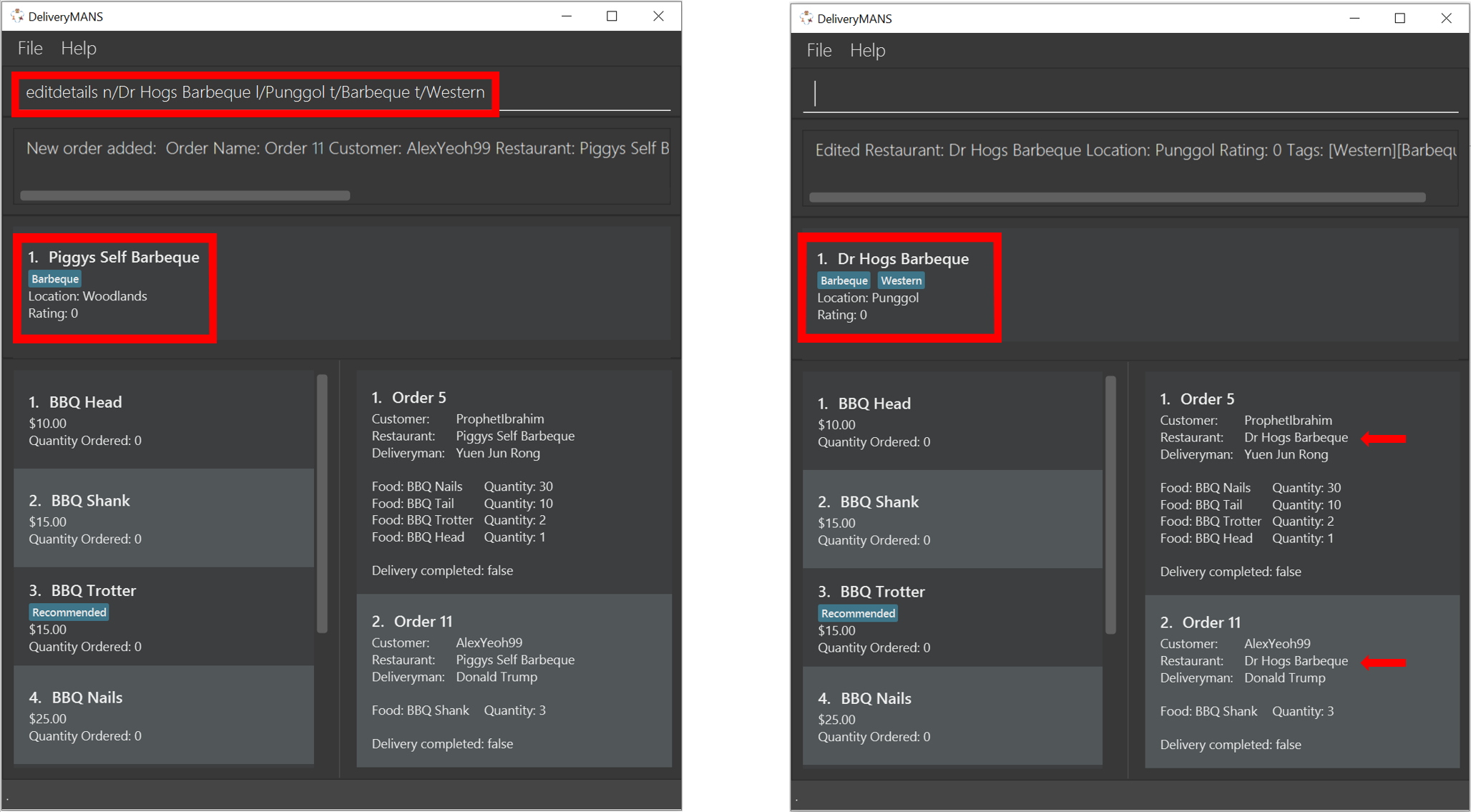
Editing restaurant’s details (under EditMode): editdetails
This command edits the details of the restaurant under EditMode.
Format: editdetails [n/NAME] [l/LOCATION] [t/TAG]…
-
At least one of the optional fields must be provided.
-
Existing values will be updated to the input values.
-
When editing tags, the existing tags of the restaurant will be removed i.e adding of tags is not cumulative.
-
You can remove all the restaurant’s tags by typing t/ without specifying any tags after it.
Example: editdetails n/Dr Hogs Barbeque l/Punggol t/Barbeque t/Western
|
Note:
|
Adding food item (under EditMode): add
This command adds a food item to the menu of the restaurant under EditMode.
Format: add n/NAME a/PRICE [t/TAG]…
-
You can only tag a food item as "Recommended".
Example: add n/Chicken a/7.90 t/Recommended
Deleting food item (under EditMode): delete
This command deletes the food item at the specified index in the menu of the restaurant under EditMode.
Format: delete INDEX
-
INDEXmust be a positive integer from 1 to n, the number of food items in the restaurant’s menu.
Example: delete 1
|
Note:
|
Adding a rating (under EditMode): rate
This command adds a rating to the restaurant under EditMode and updates the new average rating of all the ratings added to date.
Format: rate RATING
-
RATINGmust be a non-negative integer from 0 to 5.
Example: rate 4
Exiting EditMode: exitedit
This command exits EditMode for the specific restaurant and returns to the list of restaurants
Format: exitedit
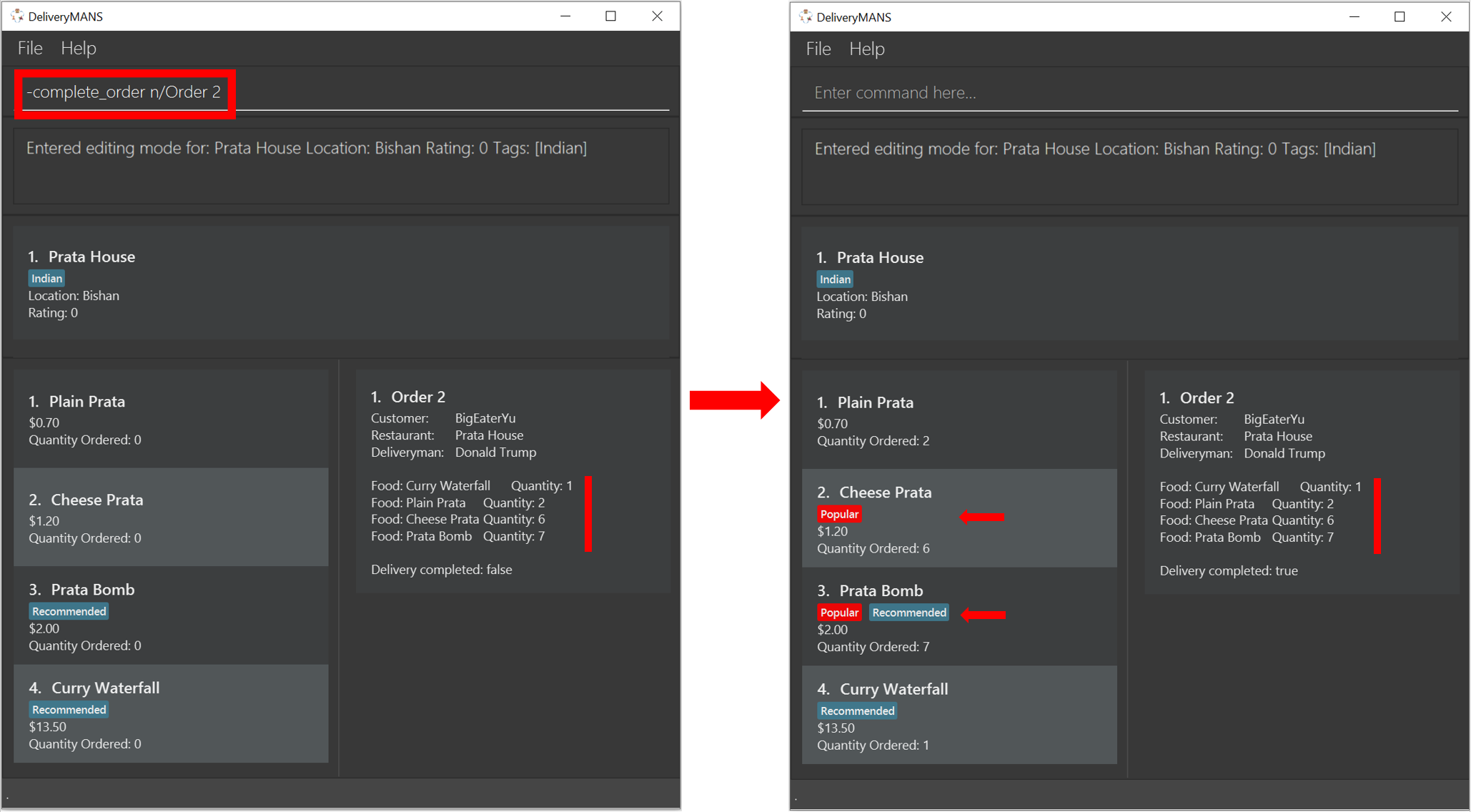
Auto-tagging of food item as "Popular"
Food items with quantity ordered more than 1.5 times the average quantity ordered of food items in the restaurant will be automatically tagged as "Popular".
Example (refer to image below):
-
16 food items are ordered in Order 2 (1 + 2 + 6 + 7), an average quantity ordered of 4 per food item.
-
Quantity ordered of food items Cheese Prata and Prata Bomb (6 and 7 respectively) is more than 1.5 times the average quantity ordered. Automatically tagged as "Popular" upon completion of Order 2.
|
Note:
|
Contributions to the Developer Guide
Given below are sections I contributed to the Developer Guide. They showcase my ability to write technical documentation and the technical depth of my contributions to the project. |
EditMode for restaurants
A Restaurant object contains many attributes. On top of a Name, Location, Rating and a list of Tag,
it also includes a list of Food as its menu, as well as a list of Order. This makes it difficult to edit
an entire Restaurant object using just one Command.
The EditMode feature allows editing of a specific Restaurant object’s details (name, location, rating, tags),
menu and orders individually under 1 interface, using different commands.
Implementation
Model:
In addition to the filteredRestaurantList that contains all the restaurants in the restaurant database,
ModelManager now contains a editingRestaurantList, which holds and allows access to the single restaurant
currently under EditMode.
When user inputs the editmode INDEX command:
-
The restaurant referenced by the
INDEXin the list of restaurants will be placed in theeditingRestaurantListvia the function callModel#setEditingRestaurant(Restaurant editingRestaurant. -
Subsequent commands that edit the restaurant, such as
AddFoodCommand,DeleteFoodCommand,AddRatingCommandandEditDetailsCommandwill create a new restaurant with the edited attributes. -
The outdated restaurant will be replaced with the new edited restaurant in both the
filteredRestaurantListandeditingRestaurantListvia the function callModel#setRestaurant(Restaurant oldRestaurant, Restaurant newRestaurant).
Logic:
The Logic for EditMode is facilitated by Context enum type, which contains the following constants:
GLOBAL, CUSTOMER, RESTAURANT, DELIVERYMEN and EDITING. It determines the Context the application is in,
as well as the commands the user can access. It is contained inside LogicManager as an attribute. EditModeCommand is only
accessible in Context.RESTAURANT, and entering a valid EditModeCommand will change the Context to Context.EDITING.
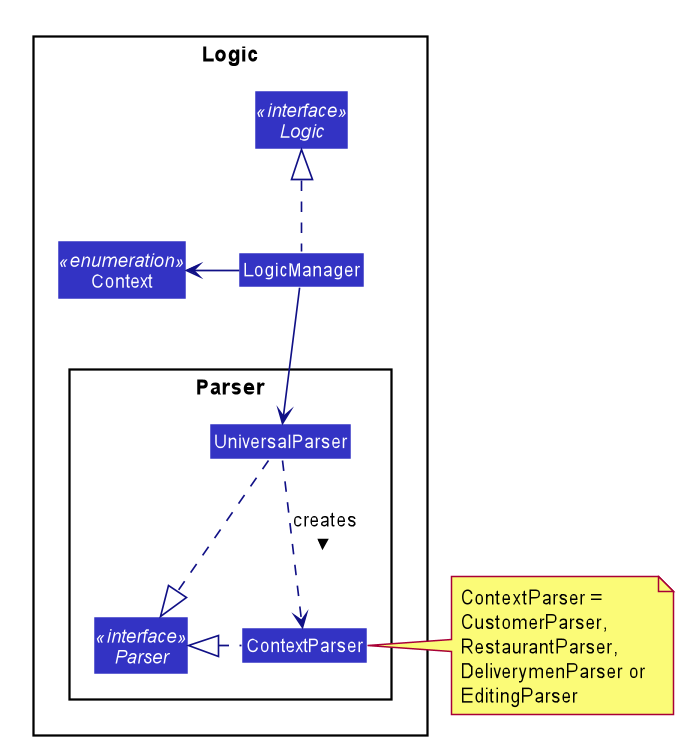
The following class diagram shows the relevant structure of Logic and Parser:
When the user inputs a command:
-
userInputwill always be parsed byUniversalParserfirst, regardless of the currentContext. The reason for this is to check for universal commands, which are accessible in allContext. -
Subsequently, if the command word in
userInputmatches none of the universal commands, thenUniversalParserwill create a context specificParserbased on the currentContext, i.e.CustomerParser,RestaurantParser,DeliverymenParser,EditingParser, which takes over and parses theuserInput. Any context switching command will then change theContextinLogicManager.
The following activity diagram summarises what happens when the user enters a command:
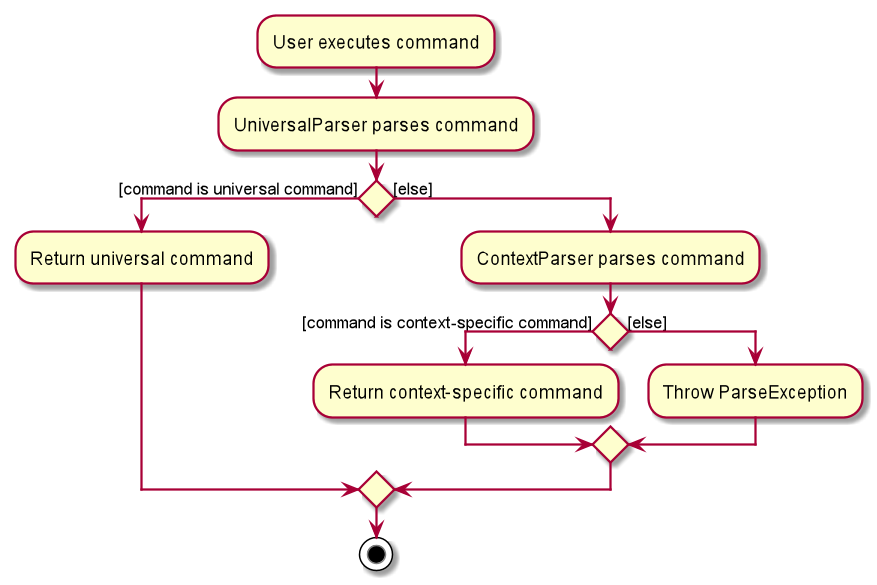
When user inputs the editmode INDEX command:
-
UniversalParserwill parse it first. -
Since
editmodematches none of the universal commands,UniversalParserwill create a newRestaurantParser(since currentContextisContext.RESTAURANTasEditModeCommandis only accessible in saidContext). -
The new
RestaurantParserwill then parse theuserInputand subsequently change theContextinLogicManagertoContext.EDITING, unlocking commands to edit the restaurant, such asAddFoodCommand,DeleteFoodCommand,AddRatingCommandandEditDetailsCommand.
UI:
Commands that change the UI will either:
-
Pass its command class to
MainWindowin the UI package if the command doesn’t change theContext -
Pass the new
ContexttoMainWindowin the UI package if the command changes theContext.
as the second parameter of the CommandResult returned by the command.
When MainWindow receives the CommandResult, it will extract out either the command class or Context from
CommandResult and make changes to the UI accordingly via the function call
MainWindow#changeDisplay(Context context) or MainWindow#changeDisplay(Class commandClassName).
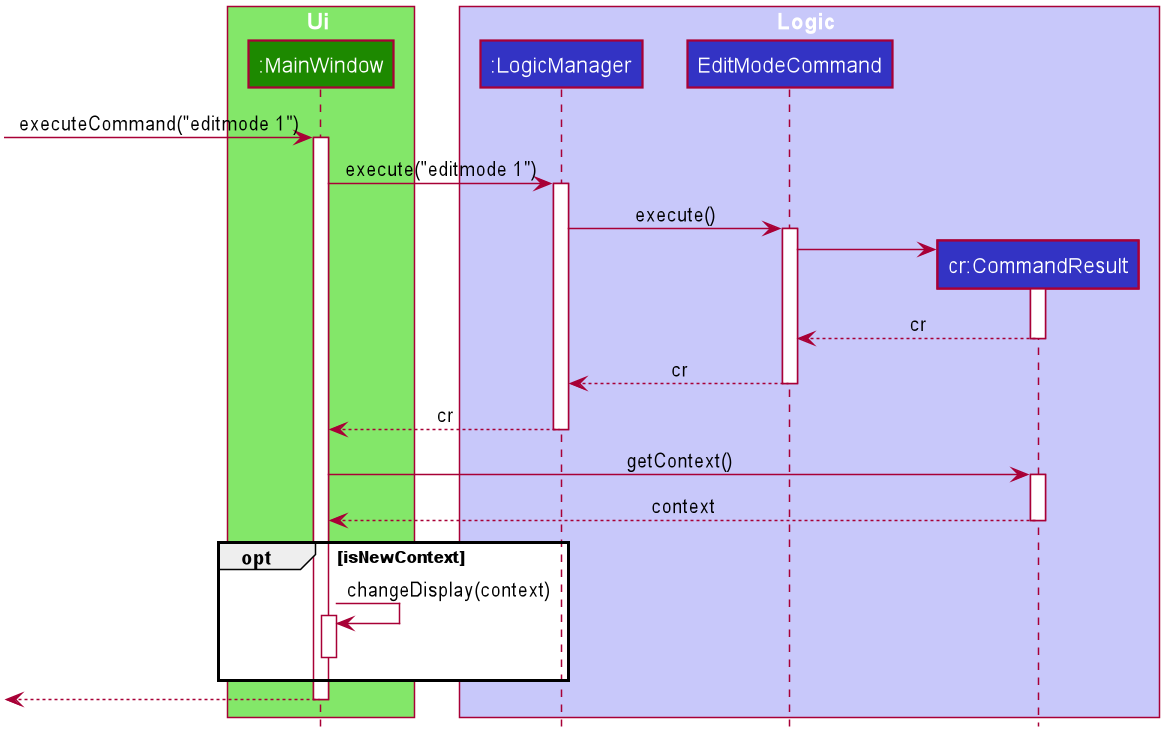
When user inputs the EditModeCommand:
-
Since
Contextis changed toContext.EDITING, it will be passed as the second parameter of theCommandResultreturned by theEditModeCommand. -
Upon receiving this new
Context,MainWindowwill call the functionchangeDisplay(Context.EDITING)to change the UI. An extraStackPaneshowing the restaurant under EditMode will be displayed, while theSplitPanedisplaying the list of restaurants originally will now be filled with the restaurant’sFoodmenu andOrderlist.
The following sequence diagram summarises how the EditModeCommand changes the UI:
Design Considerations
Aspect: Structure of Logic and Parser
-
Current:
LogicManagercontains only theUniversalParser, which then creates a context-specific parser depending on the currentContextinLogicManager.-
Pros: Checking whether
userInputis a universal command only needs to be done once inUniversalParser -
Cons: Doesn’t make as much sense for
UniversalParserto be able to create other context-specific parsers.
-
-
Alternative: Instead of containing only the
UniversalParser, which then creates the other 4 context-specific parsers,LogicManagercontains all 5 parsers.-
Pros: Makes more sense to have
LogicManagercontaining all 5 parsers which parsesuserInputindividually based on the current context. -
Cons: Checking whether
userInputis a universal command needs to be repeated in each parser.
-
Aspect: Changing of UI
-
Current: If the
Commandthat changes the UI does not change theContext, pass its command name toMainWindowinstead of creating a newContextto signal a change in UI.-
Pros: Does not create unnecessary
Context. -
Cons: 2 method signatures are needed for
MainWindow#changeDisplayto change the UI.
-
-
Alternative: A new
Contextis created for everyCommandthat changes the UI.-
Pros: Only 1 method signature is needed for
MainWindow#changeDisplayto change the UI. -
Cons: Creates many unnecessary
ContextthatLogicManagerwill never be in.
-